When it comes to learning a new language, one of the most challenging aspects can be mastering the correct pronunciation. This is especially true for the Arabic language, which has a unique set of sounds and letters that can be difficult for non-native speakers to replicate. In this guide, we will take a comprehensive look at the sounds of the Arabic language and provide tips and tricks for perfecting your pronunciation.
Understanding The Arabic Alphabet
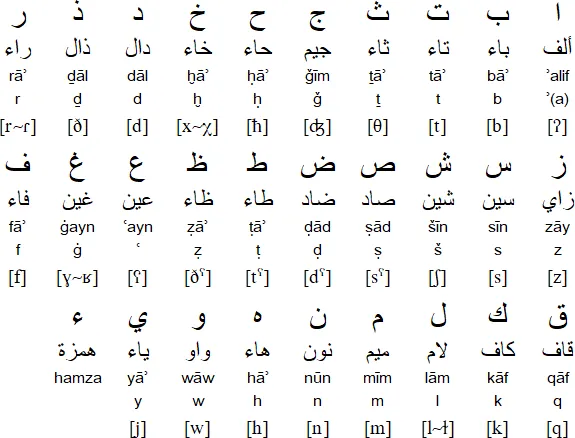
The first step in mastering Arabic pronunciation is understanding the Arabic alphabet. The Arabic alphabet is made up of 28 letters, all of which are consonants. Unlike the English alphabet, Arabic does not have separate letters for short and long vowels. Instead, vowel sounds are indicated using diacritical marks above or below the letters.
It’s important to note that the Arabic script is written from right to left, which can take some getting used to for those familiar with left-to-right scripts such as English.
Pronouncing Consonants

When it comes to consonant sounds, Arabic has several unique sounds that can be difficult for non-native speakers to replicate. One of the most challenging sounds is the “emphatic” or “glottalized” consonants, represented by the letter “ص” (ṣād) and “ض” (ḍād). These sounds are produced by adding a glottal stop to the sound of the consonant.
Another unique sound in Arabic is the “pharyngealized” consonants, represented by the letters “ح” (ḥā) and “خ” (khā). These sounds are produced by constricting the pharynx while pronouncing the sound.
It’s also important to note that the pronunciation of some consonants can change depending on their position within a word. For example, the letter “ط” (ṭā) is pronounced with an “a” sound when it comes at the beginning of a word, but with an “i” sound when it comes at the end.
Pronouncing Vowels
As mentioned earlier, Arabic does not have separate letters for short and long vowels. Instead, vowel sounds are indicated using diacritical marks above or below the letters. There are three main vowel sounds in Arabic language: “a”, “i”, and “u”.
When it comes to pronouncing these vowels, it’s important to remember that they are not pronounced as they are in English. For example, the “a” sound in Arabic is pronounced more like the “ah” sound in English. Additionally, the “i” sound is pronounced more like the “ee” sound in English, while the “u” sound is pronounced more like the “oo” sound in English.
Tips and Tricks for Mastering Pronunciation
One of the best ways to improve your Arabic pronunciation is to practice listening to native speakers and mimicking their sounds. This can be done through listening to Arabic music, watching Arabic movies and TV shows, or even talking to native speakers.
Another helpful tip is to practice with a language learning app or program that includes audio pronunciation exercises. This will allow you to hear the correct pronunciation of each sound and then practice mimicking it.
ArabianTong offers a course Reading Arabic online for adults and children. This course provides professional Arabic language teaching, how to teach grammatical rules, prepositions, and how to pronounce Arabic classical.
Finally, it’s important to be patient with yourself and not get discouraged if you have difficulty with certain sounds. Remember that mastering any new language takes time and practice.
In conclusion
mastering the sounds of the Arabic language can be challenging, but with the right tools and resources, it is definitely possible. By understanding the Arabic alphabet, practicing the unique consonant sounds, and perfecting your vowel pronunciation, you can improve your Arabic speaking and listening skills. Additionally, by listening to native speakers and using language learning resources, you can continue to build your pronunciation skills over time.
It’s also important to remember that fluency in any language is not only about pronunciation, but also about understanding grammar course, vocabulary, and cultural context. While perfecting your pronunciation is an important step in becoming fluent in Arabic, it’s also important to continue to study and practice the other aspects of the language.
In this Arabic Pronunciation Guide, we’ve provided a comprehensive overview of the sounds of the Arabic language and tips for mastering them. However, it’s important to remember that the best way to improve your pronunciation is through consistent practice and exposure to the language. So, find a language partner, immerse yourself in the culture, and keep practicing – you’ll be speaking like a native in no time.
Arabic Pronunciation FAQs
What is the Arabic alphabet made up of?
The Arabic alphabet is made up of 28 letters, all of which are consonants.
How are vowel sounds indicated in the Arabic language?
Vowel sounds are indicated using diacritical marks above or below the letters.
How do you pronounce emphatic or glottalized consonants in Arabic?
Emphatic or glottalized consonants are pronounced by adding a glottal stop to the sound of the consonant.
How does the pronunciation of some consonants change depending on their position within a word?
The pronunciation of some consonants can change depending on their position within a word. For example, the letter ط (ṭā) is pronounced with an {a} sound when it comes at the beginning of a word, but with an {i} sound when it comes at the end.
What are some tips for mastering the pronunciation of the Arabic language?
Some tips for mastering the pronunciation of the Arabic language include practicing listening to native speakers, using language learning apps or programs that include audio pronunciation exercises, and being patient with oneself and not getting discouraged if there is difficulty with certain sounds. Additionally, it is important to remember that mastering any new language takes time and practice.

